Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Taxifolin 90% To Inhibit Ovarian Cancer Cell


Taxifolin is non-mutagenic and low toxic compared to the related compound quercetin. It acts as a potential chemopreventive agent by regulating genes through an ARE-dependent mechanism. Taxifolin has been shown to inhibit ovarian cancer cell growth in a dose-dependent manner. There is also a strong correlation (with a correlation coefficient of 0.93) between the antiproliferative effects of dihydroquercetin (DHQ, taxifolin) derivatives in the skin of murine fibroblasts and human breast cancer cells.
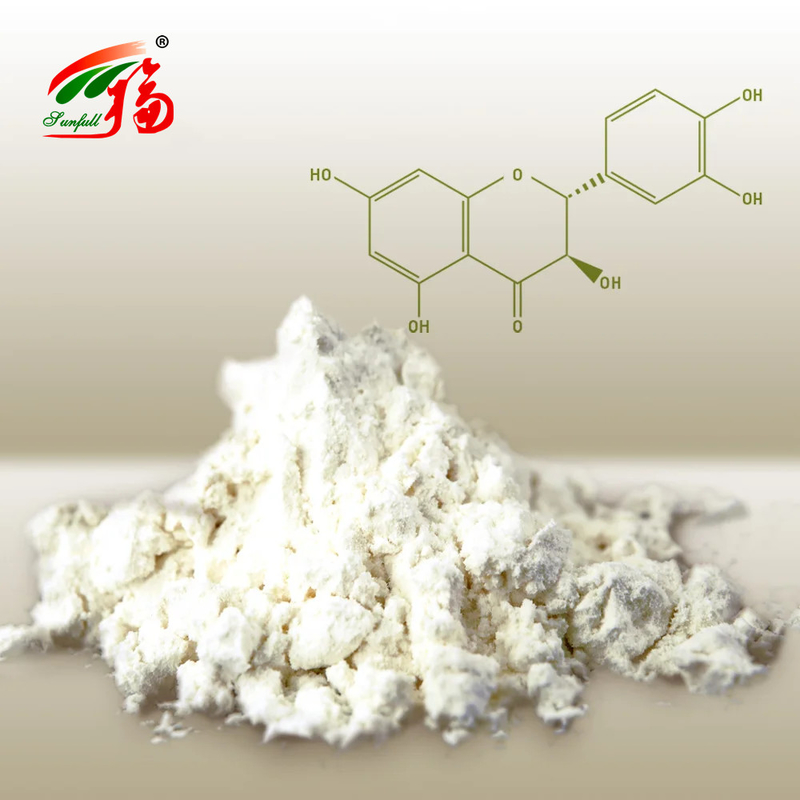
The flavonoid Taxifolin, also known as Dihydroquercetin, has similar pharmacological effects to other flavonoids. Its antioxidant capacity, however, is superior to that of common flavonoids, and it is widely distributed and abundant, which is why its medicinal value is gradually becoming recognized. In practice, It is rarely used singly, but is often used in preparations such as silymarin along with silybin A, silybin B, isosilybin A, etc. With the exploration of its resources and medicinal potential goes deeper, the therapeutic efficacy and the medical value of taxifolin is becoming unambiguous. To help the future research, this article, after a review on pharmacological activities, focuses on the breakthroughs on the applications of taxifolin in treatment of diseases across human systems from 2019 to 2022, and look ahead the future therapeutic potentials of Taxifolin.
Dihydroquercetin is a kind of chemical substance extracted from larch, Douglas fir and other pine plants. It belongs to bioflavonoid vitamin P. It is easily soluble in ethanol, acetic acid and boiling water, and slightly soluble in cold water.It has the function of antioxidation and free radical scavenging.
| Item |
Specification |
Result |
| Appearance |
Light yellow to off-white |
Conforms |
| Loss on dring |
≤5% |
2.5% |
| Ash |
≤5% |
0.5% |
| Heavy metals |
≤20ppm |
Conforms |
| Total Plate Count |
≤1,000cfu/g |
Conforms |
| Total Yeast & Mold |
≤100cfu/g |
Conforms |
| Assay |
≥90% Dihydroquercetin |
93.05% |
The structural diversity of flavonoids is thought to be an influential factor in their antioxidant activity. There is a direct link between the number of hydroxyl groups attached to the aromatic ring and the antioxidant activity of the molecule. Taxifolin is a naturally bioactive flavonoid with superior antioxidant capacity than common flavonoids, which is closely related to its phenolic hydroxyl groups. The 5- and 7-OH groups present in the A- and C-rings have a 4- oxo function, which allows taxifolin to exhibit a powerful scavenging effect on free radicals. In addition, the strong oxidative properties of Taxifolin also result from its conjugated structure and the resonance stability of the two phenolic rings. However, due to the absence of C2, C3-double bond in the C ring of taxifolin, its antioxidant activity is still slightly inferior to that of other flavonoids with identical hydroxylation pattern lacks antioxidant potency.

Function of Taxifolin
Various pharmacological properties of taxifolin especially, antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-Alzheimer, hepatoprotective and cardioprotective were found. The most important observation is taxifolin showed better activity in vitro studies. Surprisingly, taxifolin showed effective anticancer, hepatoprotective and cardioprotective activities through multiple mechanisms.
1. Dihydroquercetin is not mutagenic and low toxic compared to the related compound quercetin. It acts as a potential chemopreventive agent by regulating genes via an ARE-dependent mechanism.
2.Taxifolin inhibited the cellular melanogenesis as effectively as arbutin, one of the most widely used hypopigmenting agents in cosmetics.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!